
29% More Biogas and 51% Higher Power Generation in Anaerobic Digester with BG Max 3000
A slaughterhouse significantly improved the operation and biogas production of its waste sludge anaerobic digester with the usage of BG Max 3000.
Benefits
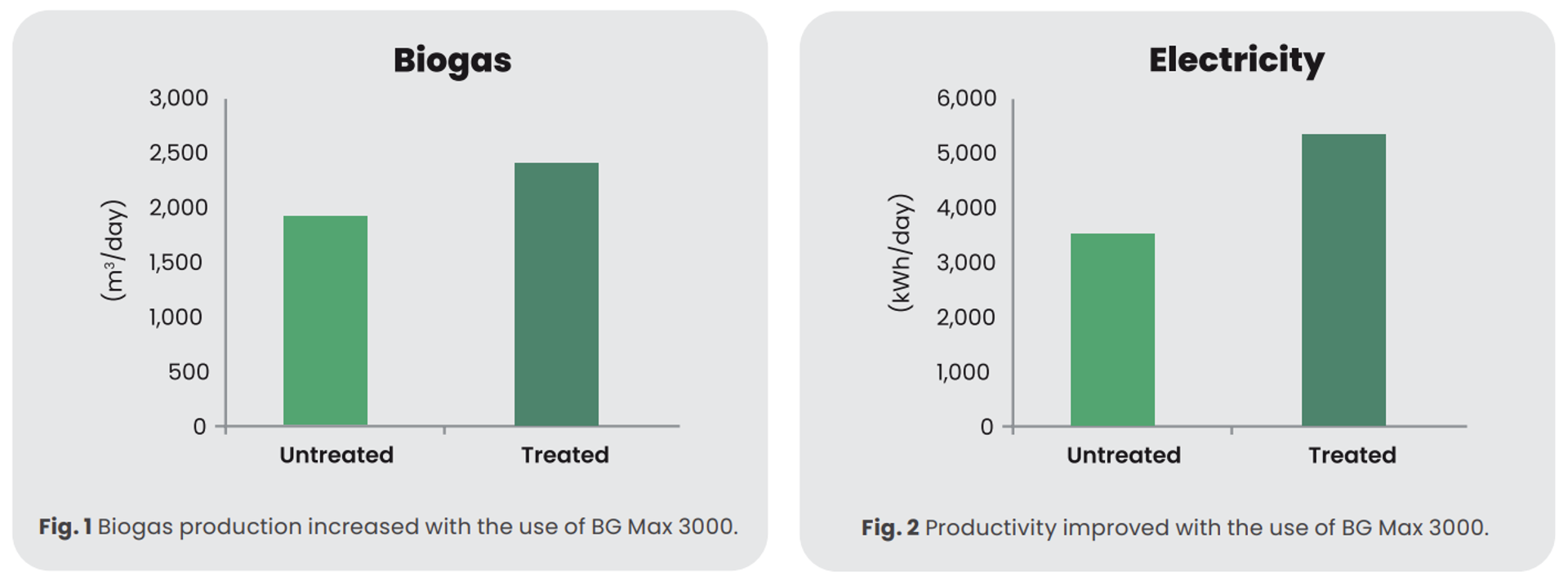
- 29% increase in overall biogas production
- Helped contribute to a 51% increase in electrical power generation
- Significant cost savings associated with increased feed efficiency
Background
The swine slaughterhouse generated a variety of organic-rich wastes that it fed to an anaerobic digester for the purpose of reducing solids and generating biogas used to heat the facility. The facility’s operators were forced to underload the digester due to poor performance during high loading operations. A biological solution was identified that would help stabilize the digester, allow for increased loadings, and improve reactor efficiency
Application
The facility processes 300 to 400 head of swine per day and operates its own wastewater treatment system. The system treats approximately 250 m3 (66,000 gallons) of wastewater per day. The treatment system includes an anaerobic digester for the treatment of biological waste-activated sludge.
In order to reduce costs associated with disposal of other solids and high-strength wastes, the facility also feeds the digester intestinal wastes, straw, blood, and manure, as well as other process wastes. The digester is fed with approximately 35–40 tons of waste per day, which contains approximately 8% total solids. In general, the digester is capable of reducing the combined bio-waste feed into a sludge that is only 1.8% in total solids (a 76% reduction in solids).
The breakdown of sludge and high-strength wastes generates a methane-rich biogas that is recovered as fuel in a combined heat and power (CHP) generator used to heat the slaughterhouse. The plant manager was satisfied with the performance of the digester in low-loading operation; however, the system had been designed to treat larger loads. By increasing the loading, the plant manager sought to improve efficiency and reduce external disposal costs. BG Max 3000, a blend of beneficial microorganisms and fast-acting enzymes, was added to the inlet of the anaerobic tank.
Results
Only one month after the beginning of the treatment, substantial improvements were noted. The customer generated an additional 538 m3 (19,000 ft3) of biogas per day, a 29% increase. Not only had the volume of biogas been increased, but the efficiency of the operation had improved sufficiently enough to allow the plant managers to increase throughput to the maximum design loading limit. As a result of greater biogas production, the rate of electrical power generation by the CHP increased by 51% (an additional 1,800 kWh/ day).
Conclusion
The addition of BG Max 3000 improved the operation and productivity of an anaerobic digester being fed sludge and slaughterhouse wastes. This resulted in:
- Improved stability of the digester operation
- Increased biogas production
- Reduced cost of waste treatment
- Decreased energy demand
- Improved sustainability
